Install Redmine 25x on Centos 65 complete » History » Revision 2
« Previous |
Revision 2/8
(diff)
| Next »
Mr. DTTH, 2014-06-25 15:42
Install Redmine on Centos 6.5 - 64 bit¶
- Table of contents
- Install Redmine on Centos 6.5 - 64 bit
- The System Requirements
- Update the System
- Install the dependencies packages
- Install Apache and MySQL
- Turn off SELinux
- Set up the Hostname
- Configuring the Firewall
- Install PHP and phpMyAdmin
- Install Ruby
- Install Rubygems
- Install Passenger
- Create Database for Redmine
- Install Redmine
- Setting up Rails
- Activate FCGI
- Setting up Apache and FastCGI
- Creating Files Directory
- Configuring Email
- Create Virtual Host for Redmine
- Running Redmine
- Install Subversion
Origin source from : eDesignNetwork.org or Wiki : Install Redmine
You can download this document as ebook format, read with the eReader program.
The System Requirements¶
During the installation process we will use the Centos 6.5 - 64 bit OS, the original hardware configuration should not require high you can install on a normal PC or a virtual machine using VMWare, VirtualBox.
For the CentOS operating system, you can downloading at URL address :
Selecting a 64-bit version called "CentOS-6.5-x86_64-bin-DVD1.iso", after you download and install on the computer or on a virtual machine, the installation process is simple for anyone with basic computer skills.
Although this guiding document install on the Centos 6.5 operating system, but you can use any version of Centos 6.x for both 32 bit and 64 bit.
When the installation process is complete, you need the tools to connect with the Centos server via FTP and SSH protocols, you must to install FileZilla at the URL address :
https://filezilla-project.org/download.php
Next, we need to install Putty to communicate with Linux via SSH.
Download the installation package Putty for Windows at the following address :
To prepare for the next section, you need to set up a connection using Putty SSH to Server running Centos, enter the IP address of the computer running Centos (probably IP on the dedicated server, on the virtual machines, on the your LAN or PC).
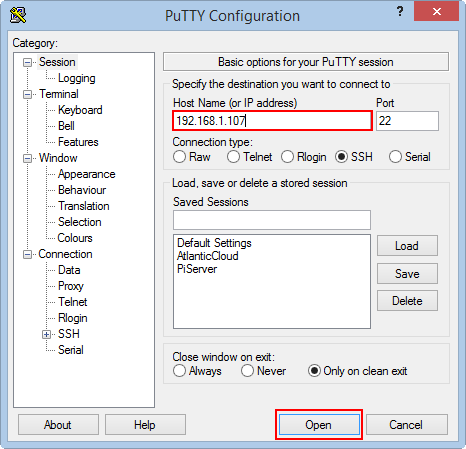
After setting up SSH connection successful, we will move on to step installing the system.
Update the System¶
For convenience in the next section, we follow the way :
- Select and copy command (CTRL + C)
- Right-click into the Putty window to Paste command and press Enter to execute
Copy and execute the following command to update the critical components of the system :
yum update
After the update completed, we need to restart the system using the following command :
rebootInstall the dependencies packages¶
These are the basic software packages for environment settings and utility tools to compile other packages in the next section.
Copy the block command and execute in the Putty Windows :
This is a long command line, copy all and implementation.
yum -y install nano zip unzip libyaml-devel zlib-devel curl-devel openssl-devel httpd-devel apr-devel apr-util-devel mysql-devel gcc ruby-devel gcc-c++ make postgresql-devel ImageMagick-devel sqlite-devel perl-LDAP mod_perl perl-Digest-SHA
Install Apache and MySQL¶
Apache is a server application for communicating over the HTTP protocol. Apache runs on operating systems such as Unix, Linux, Microsoft Windows, and other operating systems.
Apache play an important role in the development of the internet and the world wide web.
MySQL is the database management free open source most popular on the world, MySQL has high speed, stability and ease of use, portability, operating on multiple operating systems offer a large system is very powerful utility functions.
With the speed and high security, MySQL is well suited for applications that access databases on the internet.
Use the following command to install :
yum -y install httpd mysql mysql-server
Allow start services when OS boot :
chkconfig httpd on
chkconfig mysqld on
service httpd start
service mysqld start
Set the password for MySQL
/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installationBecause we not have a password for the root account so you press Enter to skip.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):Select Yes to set the password for the MySQL root account.
Set root password? [Y/n] yEnter and confirm your password, remove the anonymous user, select Yes
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] yAllow remote login to MySQL as root account, select No.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] nDelete the test database, select Yes
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] yReload privilege tables, select Yes
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] yTurn off SELinux¶
SELinux is a security feature advanced for Linux operating system, when installing the system you need to turn off this feature to get the process done smoothly, after successful you can turn on back if you want.
nano /etc/selinux/configChange the file content :
SELINUX=disabled
Press CTRL + O to save the file and press CTRL + X to exit.
Set up the Hostname¶
By default when installing a new OS Centos not set the hostname, so we need to setting with the command :
nano /etc/hosts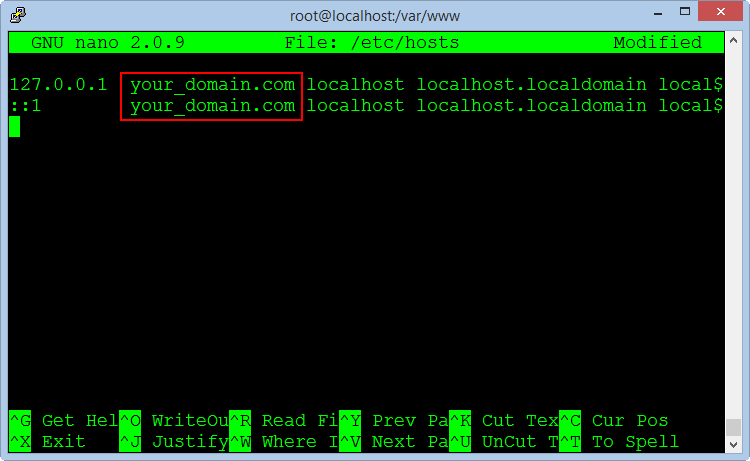
Add your domain name or host name that you set on both the command line, save the file and exit, the server name will be changed when restarting.
Configuring the Firewall¶
We do not want to turn off the firewall because it's quite important, so you need to add rules to allow port 80 for HTTP and port 443 for HTTPS.
In the Centos OS, you can configuration firewall by editing files iptables and ip6tables.
nano /etc/sysconfig/iptables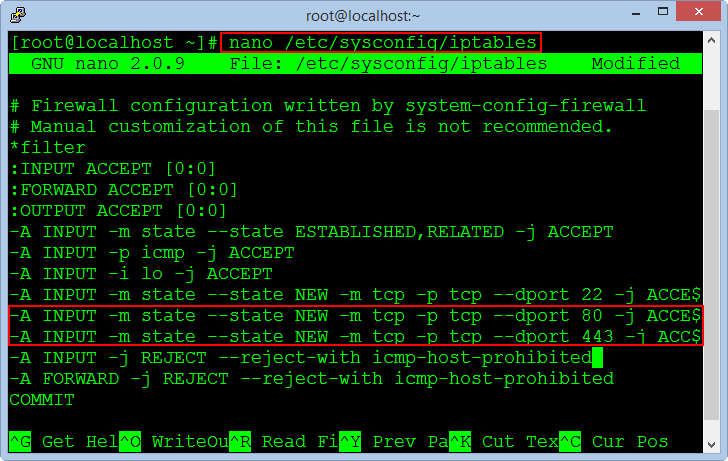
Press Enter to create a new line after the line of port 22, copy the following two commands and right click on the window to the Paste command.
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
Press CTRL + O to save the file and press CTRL + X to exit.
The same applies for IP6 firewall :
nano /etc/sysconfig/ip6tablesAdd these lines to the file.
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
After you finish editing both files, run the commands to apply the new rules for firewall.
/etc/init.d/iptables restart
/etc/init.d/ip6tables restart
Allow turn on the firewall when reboot the operating system.
chkconfig iptables on
chkconfig ip6tables on
Finally, we need to restart the system to apply the changes to the SELinux and Hostname.
rebootInstall PHP and phpMyAdmin¶
Because we use MySQL database management system, so we need to install phpMyAdmin program management.
phpMyAdmin is a free open source tool written by PHP language to manage MySQL database via a web browser.
It can create, modify or delete databases, tables, fields or records, perform SQL statements, or managing users and permissions.
The command to install PHP and the packages :
yum -y install php php-mysql php-gd php-imap php-ldap php-mbstring php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-pecl-apc php-soap
Restarting the Apache service :
service httpd restartAnd install phpMyadmin :
rpm --import http://dag.wieers.com/rpm/packages/RPM-GPG-KEY.dag.txt
yum install http://pkgs.repoforge.org/rpmforge-release/rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm
yum -y install phpmyadmin
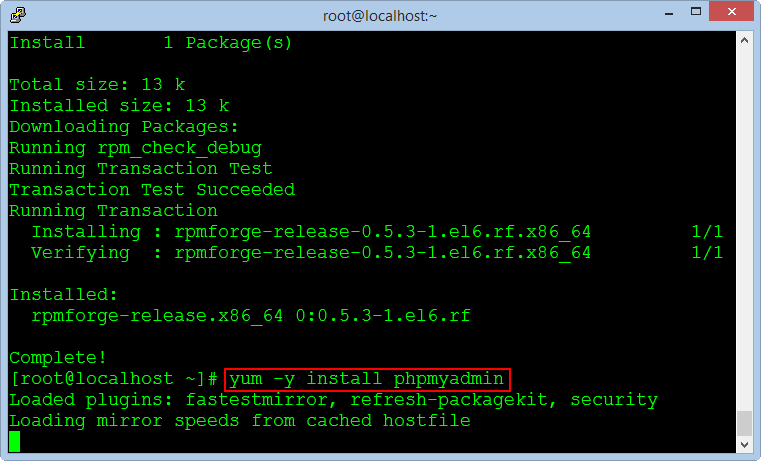
Editing the virtual host file to allow remote login to the phpMyadmin.
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpmyadmin.conf
Replace text "Allow from 127.0.0.1" to "Allow from all", save the file and exit.
Editing the configuration file for the phpMyadmin
nano /usr/share/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php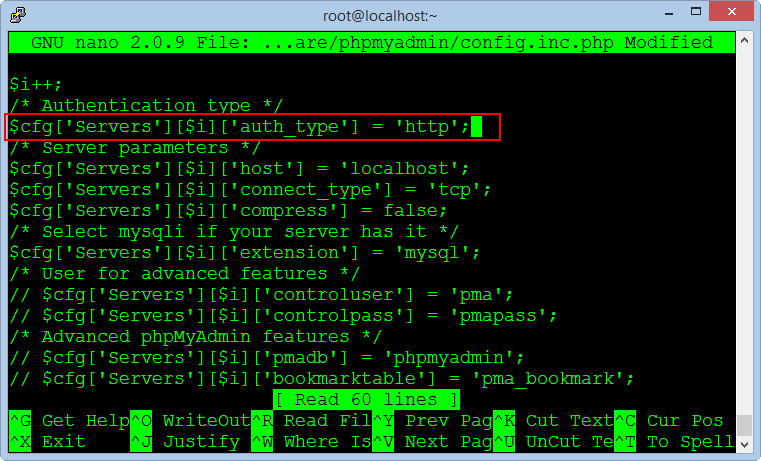
Replace text :
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['auth_type'] = 'cookie';To :
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['auth_type'] = 'http';Save the file and exit, restarting the Apache service :
service httpd restartAfter successfully installed phpMyadmin, you can check at the address :
Login with account : root / your_password
With Password has been set at step install MySQL database in the above.
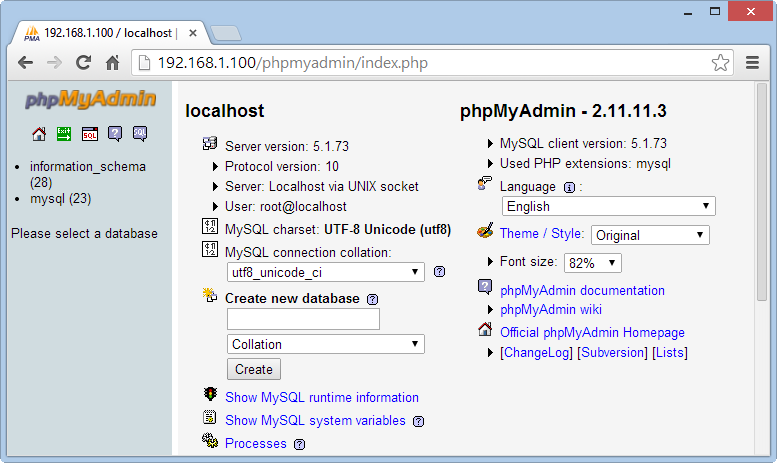
Note: If you install the Redmine system on the PC or in a virtual machine which not on the dedicated server, we need to switch the application phpMyadmin to run on port 8080 because port 80 will be used for Redmine in the next steps.
We need add a port 8080 to the firewall and change the VirtualHost for phpMyadmin.
nano /etc/sysconfig/iptables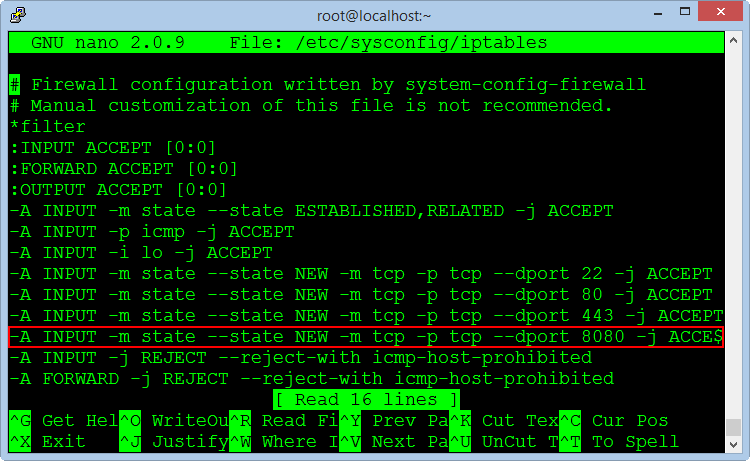
Add the command line :
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPTThe same applies for IP6 firewall :
nano /etc/sysconfig/ip6tablesAdd the command line :
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPTRestarting firewall service to allow the new port.
/etc/init.d/iptables restart
/etc/init.d/ip6tables restart
Editing the VirtualHost file to run phpMyadmin on the port 8080
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpmyadmin.conf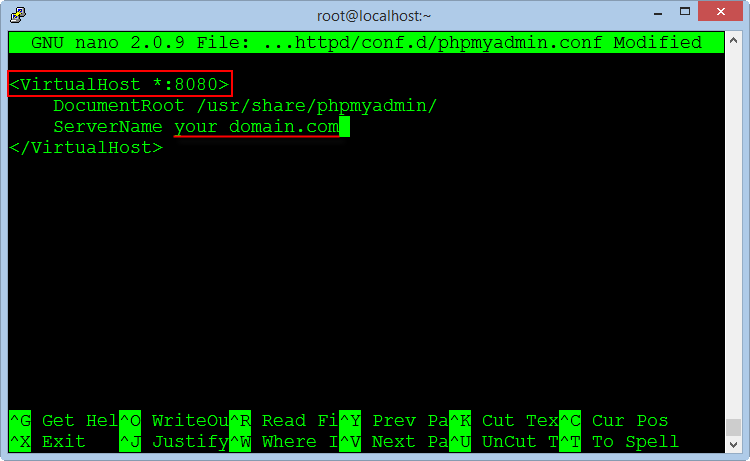
Change the file content :
<VirtualHost *:8080>
DocumentRoot /usr/share/phpmyadmin/
ServerName your_domain.com
</VirtualHost>
Next, add the command to allows listening on the port 8080 in the file "httpd.conf"
nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf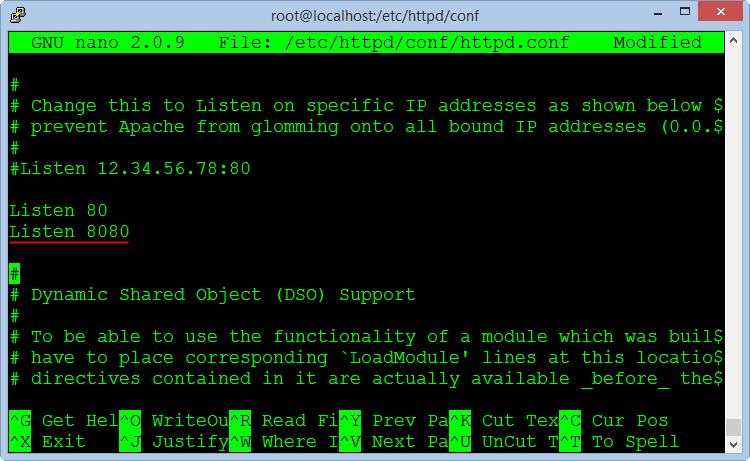
Add the command line :
Listen 8080Save the file and exit, restarting the Apache service :
service httpd restart
Now, phpMyadmin will run on the port 8080 at the address :
Install Ruby¶
Ruby is a object-oriented programming language, capable of reflection. Syntax inherited from Ada and Perl with object-oriented features of Smalltalk, and also share some features with Python, Lisp, Dylan and CLU, Ruby is a single phase interpreter.
Ruby provides programming patterns, including functional programming, object-oriented, imperative, reflective, it uses dynamic variable and automatic memory management.
Install Ruby interpreter with version management program RVM.
\curl -L https://get.rvm.io | bashAfter successful, we will launch RVM
source /etc/profile.d/rvm.shThe following command will list the versions of Ruby to install :
rvm list known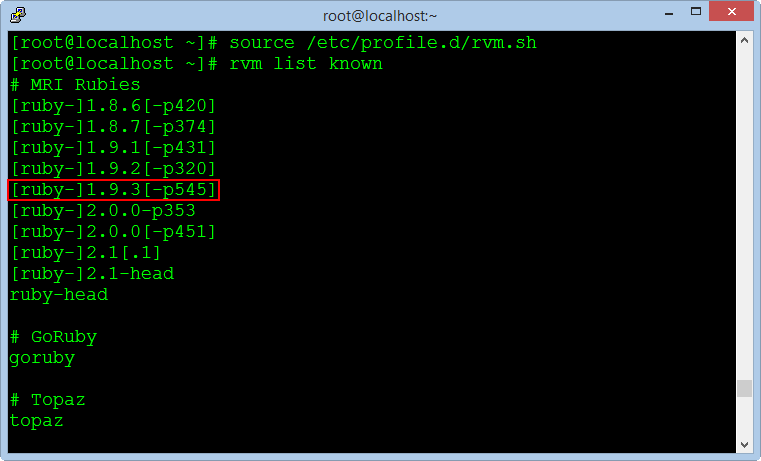
We choose the stable version [ruby-] 1.9.3 [-p545], and execute the following command :
rvm install 1.9.3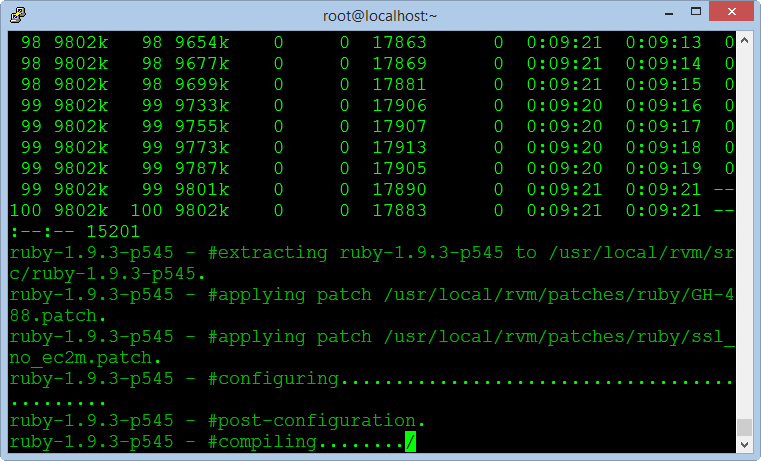
The installation process is pretty long time, but you do not need any intervention, after successful, you check with the following command :
ruby -vInstall Rubygems¶
Rubygems is a Ruby's packages management program, very popular in applications written by Ruby language and the Ruby On Rails framework.
yum -y install rubygems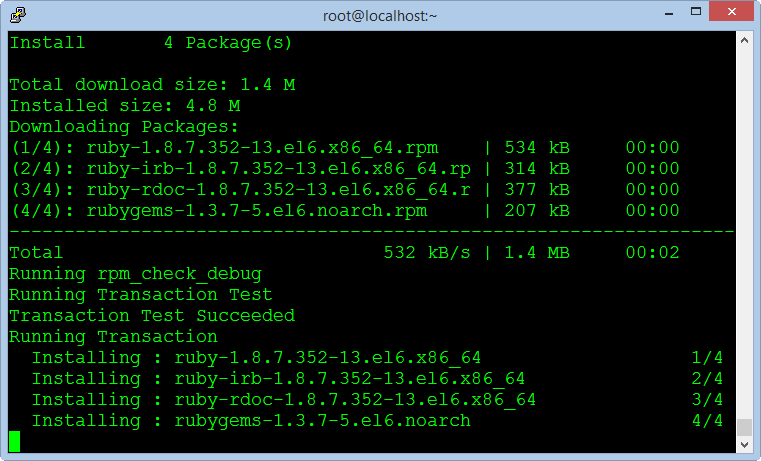
Install Passenger¶
The full name of the Passenger is Phusion Passenger, known as mod_rails or mod_rack, it is a web application intergrate with Apache and it can operate as a standalone web server support for the Ruby On Rails applications.
Execute the following commands :
gem install passenger
passenger-install-apache2-module
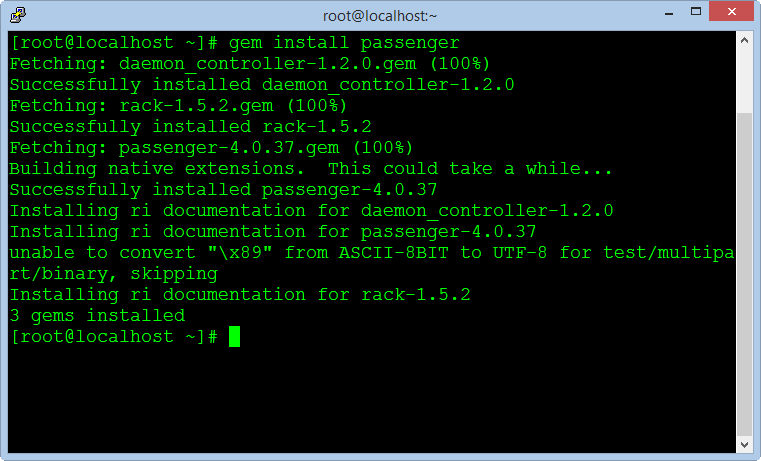
After completed, we copy a notification block in the window to create the configuration file in the next steps (select block notification and press C to copy).
LoadModule passenger_module /usr/local/rvm/gems/ruby-1.9.3-p545/gems/passenger-4.0.37/buildout/apache2/mod_passenger.so
<IfModule mod_passenger.c>
PassengerRoot /usr/local/rvm/gems/ruby-1.9.3-p545/gems/passenger-4.0.37
PassengerDefaultRuby /usr/local/rvm/gems/ruby-1.9.3-p545/wrappers/ruby
</IfModule>
Create a new virtual host file for Passenger :
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/passenger.confPaste the command blocks into the empty file and save it, then restart the Apache service.
service httpd restartCreate Database for Redmine¶
Use MySQLAdmin to create an empty database for Redmine, saved password to fill in the configuration file in the next steps.
mysql --user=root --password=root_password_mysql
create database redmine_db character set utf8;
create user 'redmine_admin'@'localhost' identified by 'your_new_password';
grant all privileges on redmine_db.* to 'redmine_admin'@'localhost';
quit;

Install Redmine¶
Redmine is a main program of the project management system, we will download and install the program from the website of Redmine.
Download Redmine version 2.5.x to directory "/var/www" on the Centos OS.
cd /var/www
wget http://www.redmine.org/releases/redmine-2.5.0.tar.gz
Extract the folder and rename directory
tar xvfz redmine-2.5.0.tar.gz
mv redmine-2.5.0 redmine
rm -rf redmine-2.5.0.tar.gz
Configuring the Database
The next, we need to configure the database was created from the above steps.
cd /var/www/redmine/config
cp database.yml.example database.yml
nano database.yml
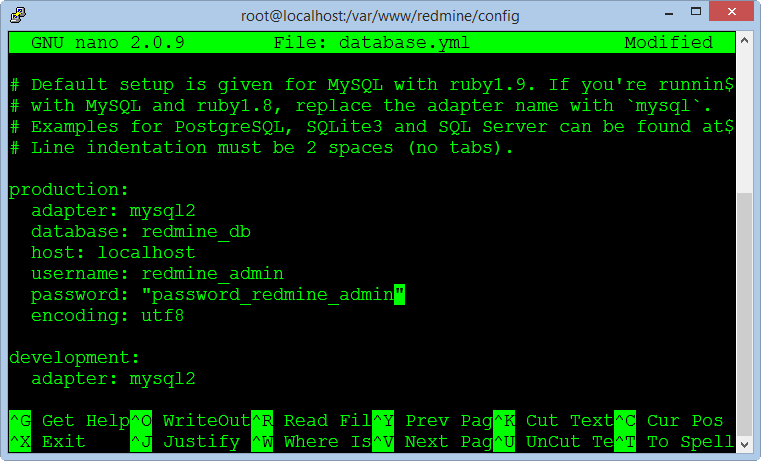
Enter name for database, enter username and password of the database. Press CTRL + O to save the file and CTRL + X to exit.
Setting up Rails¶
Install the package library support for Rails using the Bundle.
cd /var/www/redmine
gem install bundler
bundle install
rake generate_secret_token
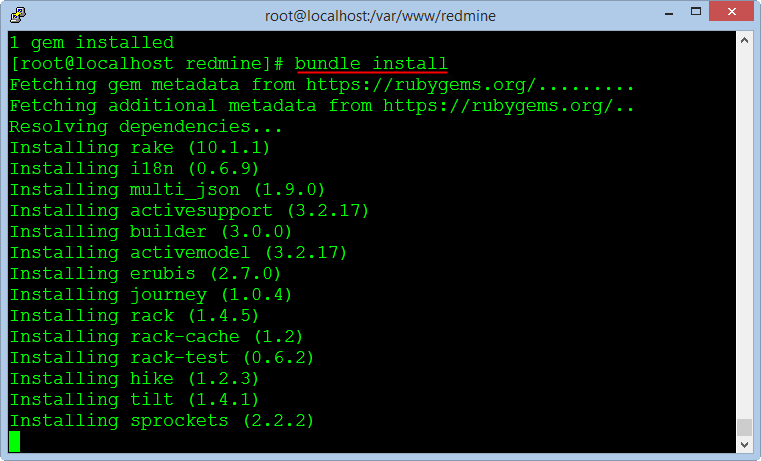
The next, we create the database table for the Redmine application.
RAILS_ENV=production rake db:migrate
RAILS_ENV=production rake redmine:load_default_data
Activate FCGI¶
cd /var/www/redmine/public
mkdir plugin_assets
cp dispatch.fcgi.example dispatch.fcgi
cp htaccess.fcgi.example .htaccess
Setting up Apache and FastCGI¶
cd /var/www/
rpm --import https://fedoraproject.org/static/0608B895.txt
wget http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
yum -y install mod_fcgid
rm -rf epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Creating Files Directory¶
This directory contains data files generated during the operation of Redmine as document or image file, we create a new directory in the "/opt".
mkdir -p /opt/redmine/files
chown -R apache:apache /opt/redmine
cd /var/www/redmine/config
cp configuration.yml.example configuration.yml
nano configuration.yml
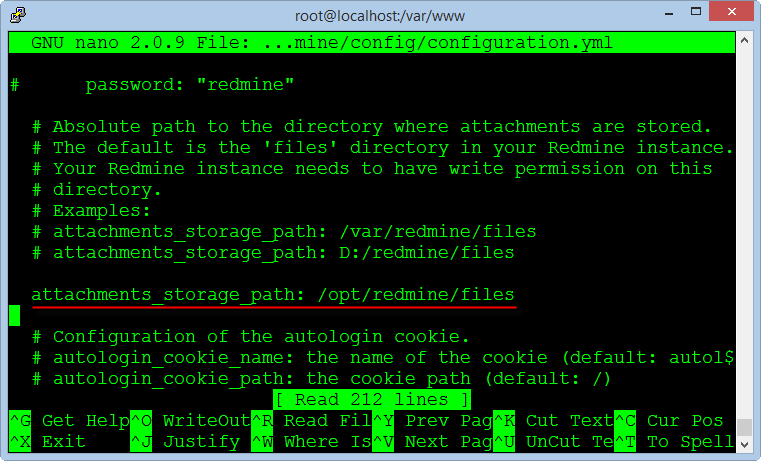
Enter the directory path containing the data files you just created in the previous step into the line "attachments_storage_path".
Note: You must add a space at the begin of the path "/opt/redmine/files" after character ":"
Configuring Email¶
Another very important function of Redmine is using email to notify members when the contents of each project changes, Redmine can use many different methods to send email that is Sendmail, SMTP, GMail ...
To configure the email we will edit the configuration file.
nano /var/www/redmine/config/configuration.ymlThe simplest is you use features of the default SendMail in the Centos OS by settings :
email_delivery:
delivery_method: :sendmail
Note : Do not use the Tab key to indent when editing the configuration file, you need to use the space bar on the keyboard.
If you use GMail's SMTP, you need to register an email account with the login methods used password normal and disable two-step authentication by smart phone.
Enter your Gmail account as below :
email_delivery:
delivery_method: :smtp
smtp_settings:
enable_starttls_auto: true
address: "smtp.gmail.com"
port: 587
domain: "smtp.gmail.com"
authentication: :plain
user_name: "your_email@gmail.com"
password: "your_password"
Save the file configuration and exit.
Create Virtual Host for Redmine¶
Create an Apache configuration file for the Redmine application at the port 80.
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/redmine.confCopy the text below and paste into the editor window, note the information to change your domain name.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName your_domain
ServerAdmin your_domain@domain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/redmine/public/
ErrorLog logs/redmine_error_log
<Directory "/var/www/redmine/public/">
Options Indexes ExecCGI FollowSymLinks
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
AllowOverride all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Save the file configuration and exit.
Running Redmine¶
Before execute Redmine in the first time, we must permission for the directory installed Redmine and restart Apache service.
cd /var/www
chown -R apache:apache redmine
chmod -R 755 redmine
service httpd restart
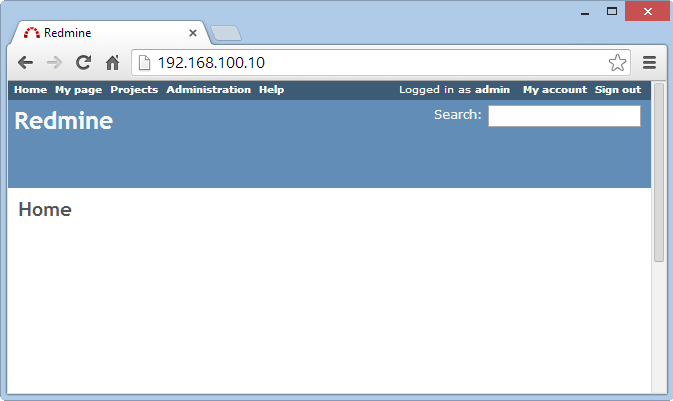
Redmine will run at the following address URL :
Login to system with an administrator account : admin / admin
You can change your password after successful login.
We can see Redmine has running but very primitive, in the next steps we will install the support plugins and customized Redmine to use professional.
Install Subversion¶
Subversion, also known as SVN, it is a version management system is very popular and easy to use, most programmers can use it competently.
We need to create a folder to store data for Redmine, the following command creates a directory and permissions for the Apache service.
mkdir -p /opt/repositories/svn
chown -R apache:apache /opt/repositories/
chmod 0755 /opt/repositories
The following command install Subversion and the packages :
yum install mod_dav_svn subversion subversion-ruby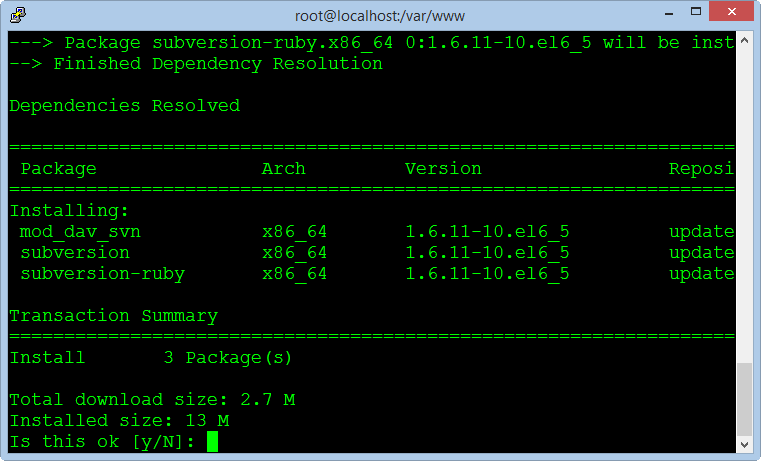
The next, we will create a directory and copy the file called "Redmine.pm", it responsible for interface data repository with Redmine and it is written by Perl language programming.
mkdir /usr/lib64/perl5/vendor_perl/Apache
ln -s /var/www/redmine/extra/svn/Redmine.pm /usr/lib64/perl5/vendor_perl/Apache/Redmine.pm
Note : If you are using 32 bit Centos, change the path "/usr/lib64" to "/usr/lib"
After installation is complete, from the Redmine application, go to the page Administration> Settings> Repositories to check the results.
To support the authentication and access to data repository for each member, we need to create a virtual host for the Apache service can access Redmine database.
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/subversion.confAdd the following lines to the end and still retain the old contents of the file :
PerlLoadModule Apache::Redmine
<Location /svn>
DAV svn
SVNParentPath "/opt/repositories/svn"
SVNListParentPath on
Order deny,allow
Deny from all
Satisfy any
LimitXMLRequestBody 0
SVNPathAuthz off
PerlAccessHandler Apache::Authn::Redmine::access_handler
PerlAuthenHandler Apache::Authn::Redmine::authen_handler
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Subversion Repository"
Require valid-user
RedmineDSN "DBI:mysql:database=redmine_db;host=localhost:3306"
RedmineDbUser "redmine_admin"
RedmineDbPass "your_password_database_redmine"
</Location>
Note : You need to change the password in the "RedmineDbPass" to correct the database password of Redmine.
At this point, we have finished the basic settings for Redmine.
Thank you!
Updated by Mr. DTTH over 11 years ago · 2 revisions