RedmineSettings » History » Revision 43
« Previous |
Revision 43/76
(diff)
| Next »
Ben Blanco, 2016-01-05 10:44
Application Settings¶
- Table of contents
- Application Settings
General settings¶
Application title¶
Title which appears in heading of the application. This is the link just under the little bar with « Home/My page/Projects/Help» when you're logged in.
Welcome text¶
Text displayed on the home page of Redmine. This text can contain HTML tags.
Attachment max. size¶
Maximum size of uploaded files (in kibi-bytes). Default: 5120 (i.e. 5 mebi-bytes )
Objects per page options¶
Here you can configure the fixed values which users can select for the amount of objects (issues, commits etc.) which are displayed per page.
Default: 25, 50, 100
Days displayed on project activity¶
The initial (and recurring while browsing) amount of days of which the project(s)-activity is shown in the activity-tab.
Host name and path¶
Host name and path of your redmine server. This name is used to write URL in emails sent to users. i.e.: the hostname of this precise redmine is redmine.org.
Protocol¶
Protocol used to generate links in email notifications. Default: http
Links in email are "guessed", but can't determine whether you're using an unsecure web server (http) or a secure one (https -> http over SSL).
Text formatting¶
Formatting method applied to the "description" fields of the issues, news, documents...
Cache formatted text (1.0)¶
Text formatting tranforms raw text to HTML and runs each time a formatted text is sent to a user's browser (eg. issue description, wiki page...), and this process can be slow with large pages or texts.
This setting lets you enable caching of formatted text.
In order to use this feature you also need to specify a cache store, such as config.action_controller.cache_store = :memory_store, which you configure by adding this setting to your config/environments/production.rb, for example:
config.consider_all_requests_local = false config.action_controller.perform_caching = true # Now here we specify which cache store we want redmine to use: config.action_controller.cache_store = :memory_store
By default, this cache store is MemoryStore.
If RAM memory usage on your server is a concern, it's highly recommended that you configure the cache to use another cache store like MemCacheStore or FileStore.
You can read more about cache stores in the Rails guides:
http://guides.rubyonrails.org/caching_with_rails.html#cache-stores
Wiki history compression¶
Lets you activate compression for wiki history storage (reduces database size). Default: disabled
Feed content limit¶
Maximum number of records contained in RSS feeds. Default: 15
Max size of text files displayed inline KB¶
It provides a way to limit the maximum size of text files which are display inline.
Max number of diff lines displayed¶
It provides a way to limit the maximum number of diff lines which are displayed by Redmine.
Display¶
Theme¶
This option lets you choose a custom theme.Redmine is shipped with two additional themes besides the default theme:
- alternate, which mainly provides issue list colorization based on issues priority.
- classic, which is derived from the Redmine 0.5.1 design and brings a classic look.
Screenshot of the alternate theme:
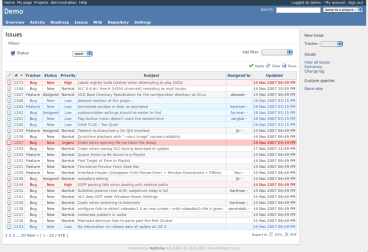
Themes are located in public/themes/. You can read more about Themes.
Default language¶
The default language is selected when the application could not determine the user's browser language. The default language is also used when sending email to multiple users. Default: English
Date format¶
Lets you choose how dates are displayed:
- Based on user's language: dates will be displayed specifically for each user, according to the format defined for its language
- Other formats: dates will always be displayed using the specified format
Default: Based on user's language
Time format¶
Lets you choose how times are displayed:
- Based on user's language: times will be displayed specifically for each user, according to the format defined for its language
- Other formats: times will always be displayed using the specified format
Default: Based on user's language
Users display format¶
Lets you choose how usernames are displayed. The following combinations are provided:
- Firstname
- Firstname Surname
- Surname Firstname
- Surname, Firstname
- Username
Use Gravatar user icons¶
If enabled, users Gravatars (globally recognized avatar) will be displayed in several places.
Default Gravatar image¶
The image to use for users who don't have a Gravatar.
Authentication¶
Authentication required¶
If this option is checked, no page of the application is accessible to anonymous users. Users must sign in to access the application. Default: No
Autologin¶
This option let users use the auto-login feature. Default: Disabled
Self-registration¶
This option lets you enable/disable new users self registration:
- disabled: users are not allowed to register
- account activation by email: new users receive an email containing a link used to activate their accounts (users must provide a valid email address).
- manual account activation (default): new users' accounts are created but need administrator approval. Administrators receive an email informing them that an account is pending their approval.
- automatic account activation: new users can log in as soon as they have registered.
Minimum password length¶
Let's the admin decide on the minimum length of the chosen passwords.
Default: 8
Lost password¶
If this option is checked, lost password functionality is available. Default: Yes
Allow OpenID login and registration¶
Provides the admin a way to disable OpenID logins and registrations.
Note that the setting is immutable as long as the dependency for the feature (an installed copy of the ruby-openid gem) is not met. You can simply install it using gem install ruby-openid.
Session expiration¶
Session maximum lifetime: Lets the administrator set the maximum lifetime of the session
Session inactivity timeout: Lets the administrator specify after how many hors of inactivity the session times out.
Warning 1: Changing these settings may expire the current sessions (including your own).
Warning 2: Redmine uses the rails cookiestore for session management. We strongly advise you to set a maximum session lifetime. If you don't, it is theoretically possible that an attacker steals the session cookie and re-uses it.
Projects¶
New projects are public by default¶
The default state of newly created projects. The project can still be made non-public while creating new project or after the creation of the project.
Generate sequential project identifiers¶
This setting will let Redmine propose sequential project identifiers for you. This can still be manually changed only while creating the project, not afterward.
Role given to a non-admin user who creates a project¶
Defines which role is given by default to a non-admin user who creates a project (this only applies when you have configured Redmine permissions in such a way that non-admin users are actually privileged to create projects).
Issue tracking¶
Allow cross-project issue relations¶
If set to Yes, relations between issues from different projects can be created. Default: No
Allow cross-project subtasks¶
Define some limits for subtasking. Definitions used are the same as version sharing, documented in RedmineProjectSettings. Default: With project tree
Options are:disabled: a parent task can only have subtasks in the same project.With all projects: a parent task can have subtasks in any other project.With project tree: a parent task can have subtasks in the same project, ancestor projects and all their descendants (e.g. also "sibling projects", "cousin projects", etc.).With project hierarchy: a parent task can have subtasks in the same project, subprojects, or ancestor projects.With subprojects: a parent task can only have subtasks in the same project or subprojects (not in parent projects or unrelated projects).
Display subprojects issues on main projects by default¶
If set to true, subprojects issues will be displayed by default on the issue list, calendar and gantt of the main projects (Since r1198). Default: Yes
Calculate the issue done ratio¶
Defines how the Issue Done Percentage is set.
- Use the issue field (default): Users can manually set % done.
- Use the issue status: Each issue status can be assigned a percentage. This enables the "% Done" option for issues and the "Update issue done ratios" command in the issue statuses overview.
Issues export limit¶
Maximum number of issues contained in CSV and PDF exports. Default: 500
Default columns displayed on the issue list¶
This setting lets you define which columns are displayed on the issue lists by default.
Only custom fields that are marked as 'For all projects' can be selected here.
Email notifications¶
Emission mail address¶
Email address used in the "From" field of messages sent to users.
Blind carbon copy recipients (bcc)¶
If set to true, email notification will be sent as Blind carbon copy. Default: Yes
Plain text mail¶
If set to true, emails are sent in plain text only (no HTML).
Emails footer¶
Here you can enter some text that will be appended to the emails sent by the application.
Incoming emails¶
See for detailed instructions about these settings RedmineReceivingEmails.
Truncate emails after one of these lines¶
These setting can be used to remove signatures from incoming emails.
Enable WS for incoming emails¶
Redmine can be configured to allow issue creation or comments via email. In order to use that feature, you have to enable the API that receives emails. That is where this setting is for. Default: Off
API key¶
Within this setting you can enter a secret key used for the issue creation or comments via email feature.
Repositories¶
Enabled SCM¶
Here you can (de)select the SCM-systems Redmine should "provide" to the individual projects. This setting is useful if you only support several SCM-systems (e.g. only Git or only SVN).
Fetch commits automatically¶
If this option is activated, the application automatically retrieves the new revisions when a user consults the repository.
Default: Yes
You can disable this option and automate the call to Repository#fetch_changesets using cron to regularly retrieve the revisions for all of the repositories in the background.
Example:
ruby script/runner "Repository.fetch_changesets" -e production
For Redmine 2.x:
ruby script/rails runner "Repository.fetch_changesets" -e production
For Redmine 3.x:
bin/rails runner "Repository.fetch_changesets" -e production
You can also call this task from your repository in a post-commit or post-receive hook, so that changesets are fetched after each commit.
Here is a tutorial for doing so with git: http://www.barricane.com/remine-git-post-receive.html
Enable WS for repository management¶
This option should be activated only if you installed the script for automatic SVN repository creation. Default: No
Repositories encodings¶
This option lets you specify preferred encodings for repository files (multiple values allowed, comma separated). These encodings are used to convert files content and diff to UTF-8 so that they're properly displayed in the browser.
When entering multiple encodings, the first valid encoding regarding the file content is used.
For French users, this option can be for example set to:
UTF-8, ISO 8859-15, CP1252For Japanese users:
ISO-2022-JP, EUC-JP, UTF-8, SHIF_JIS, WINDOWS-31JMaximum number of revisions displayed on file log¶
It provides a way to limit the amount of revisions which are retrieved from the SCM for a certain, browsed path.
Referencing issues in commit messages¶
When fetched from the repositories, commit messages are scanned for referenced or fixed issue IDs.
These options lets you define keywords that can be used in commit message to reference or fix issues automatically, and the status to apply to fixed issues.
Default keywords are:
- for referencing issues: refs, references, IssueID
- for fixing issues: fixes, closes
There's no default status defined for fixed issue. You'll have to specify it if you want to enable auto closure of issues.
If you want to reference issues without using keywords, enter a single star: * in the Referencing keywords (Administration/Repository) setting. In this case, any issue ID found in the message will be linked to the changeset.
Example of a working commit message using default keywords:
This commit refs #1, #2 and fixes #3This message would reference issues 1 and 2 and automatically fix issue 3.
After a keyword issue IDs can be separated with a space, a comma or &.
The keywords are caseinsensitive and at least one blankspace or colon is needed between the keyword and the first hash to produce
a match. More examples that will produce the same result as the example above:
This commit refs:#1, #2 and fixes #3 This commit Refs #1, #2 and fixes #3 This commit REFS: #1, #2 and fixes #3
Enable time logging¶
Allows time logging directly from commit messages. This only makes sense if you activated the "Time tracking" module in said project. In this case, you can add special words in your commit message to indicate the time you spent on an issue.
The basic syntax for doing that is : @<time>, where time consists in a number of hours or minutes.
Here's a list of many valid commit messages that would work if you want to say you spent N hours on issue 1234:
Implement feature #1234 @2 Implement feature #1234 @2h Implement feature #1234 @2hours Implement feature #1234 @15m Implement feature #1234 @15min Implement feature #1234 @3h15 Implement feature #1234 @3h15m Implement feature #1234 @3:15 Implement feature #1234 @3.25 Implement feature #1234 @3.25h Implement feature #1234 @3,25 Implement feature #1234 @3,25h
Activity for logged time¶
This is the type of activity that should be used when detecting there's a log time in a commit message (see above).
Updated by Ben Blanco over 9 years ago · 43 revisions